Bubble chamber


A bubble chamber is a vessel filled with a superheated transparent liquid (most often liquid hydrogen) used to detect electrically charged particles moving through it. It was invented in 1952 by Donald A. Glaser,[1] for which he was awarded the 1960 Nobel Prize in Physics.[2] Anecdotally, Glaser was inspired by the bubbles in a glass of beer; however, in a 2006 talk, he refuted this story, saying that although beer was not the inspiration for the bubble chamber, he did experiments using beer to fill early prototypes.[3]
Cloud chambers work on the same principles as bubble chambers, only they are based on supercooled gas rather than superheated liquid. While bubble chambers were extensively used in the past, they have now mostly been supplanted by wire chambers and spark chambers. Notable bubble chambers include the Big European Bubble Chamber (BEBC) and Gargamelle.
Contents |
Function and use
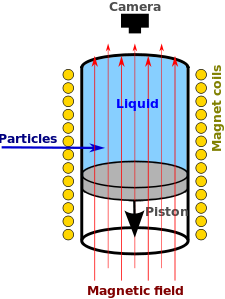
The bubble chamber is similar to a cloud chamber in application and basic principle. It is normally made by filling a large cylinder with a liquid heated to just below its boiling point. As particles enter the chamber, a piston suddenly decreases its pressure, and the liquid enters into a superheated, metastable phase. Charged particles create an ionisation track, around which the liquid vaporises, forming microscopic bubbles. Bubble density around a track is proportional to a particle's energy loss.
Bubbles grow in size as the chamber expands, until they are large enough to be seen or photographed. Several cameras are mounted around it, allowing a three-dimensional image of an event to be captured. Bubble chambers with resolutions down to a few μm have been operated.
The entire chamber is subject to a constant magnetic field, which causes charged particles to travel in helical paths whose radius is determined by their charge-to-mass ratios. Since the magnitude of the charge of all known charged, long-lived subatomic particles is the same as that of an electron, their radius of curvature must be proportional to their momentum. Thus, by measuring their radius of curvature, their momentum can be determined.
Notable discoveries made by bubble chamber include the discovery of weak neutral currents at Gargamelle in 1973,[4] which establish the soundness of the electroweak theory and paved the way to the discovery of the W and Z bosons in 1983 (at the UA1 and UA2 experiments). Recently, bubble chambers have been used in research on WIMPs, at COUPP and PICASSO.[5][6]
Drawbacks
Although bubble chambers were very successful in the past, they are of only limited use in current very-high-energy experiments, for a variety of reasons:
- The need for a photographic readout rather than three-dimensional electronic data makes it less convenient, especially in experiments which must be reset, repeated and analyzed many times.
- The superheated phase must be ready at the precise moment of collision, which complicates the detection of short-lived particles.
- Bubble chambers are neither large nor massive enough to analyze high-energy collisions, where all products should be contained inside the detector.
- The high-energy particles' path radii may be too large to allow the precise estimation of momentum in a relatively small chamber.
Due to these issues, bubble chambers have largely been replaced by wire chambers, which allow particle energies to be measured at the same time. Another alternative technique is the spark chamber.
Notes
- ↑ Donald A. Glaser (1952). "Some Effects of Ionizing Radiation on the Formation of Bubbles in Liquids". Physical Review 87 (4): 665–665. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.87.665.
- ↑ "The Nobel Prize in Physics 1960". The Nobel Foundation. http://nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/physics/laureates/1960/. Retrieved 2009-10-03.
- ↑ Anne Pinckard (21 July 2006). "Front Seat to History: Summer Lecture Series Kicks Off – Invention and History of the Bubble Chamber". Berkeley Lab View Archive. Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory. http://www.lbl.gov/Publications/Currents/Archive/Jul-21-2006.html#6. Retrieved 2009-10-03.
- ↑ "1973: Neutral currents are revealed". CERN. http://public.web.cern.ch/public/en/About/History73-en.html. Retrieved 2009-10-03.
- ↑ "COUPP experiment – E961". COUPP. http://www-coupp.fnal.gov/. Retrieved 2009-10-03.
- ↑ "The PICASSO experiment". PICASSO. http://www.picassoexperiment.ca/experiment.php. Retrieved 2009-10-03.